Mining Operation and Process: Focus on Copper Mines
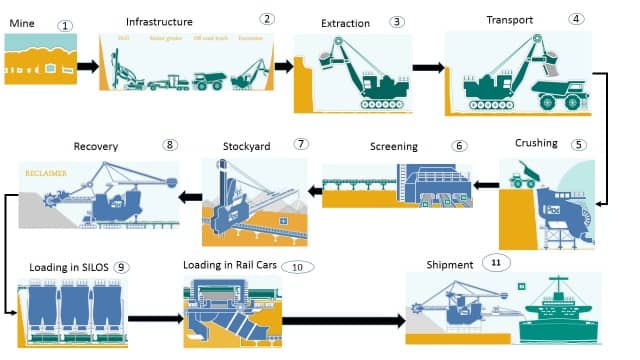
Mining, especially copper mining, is a complex operation that involves various stages from exploration to production. The process of extracting copper from the earth requires meticulous planning, precision, and a range of specialized equipment. Let’s delve into the specifics of copper mining operations and processes.
Exploration Phase
The initial step in any mining operation is the exploration phase. Geological surveys are conducted to identify potential copper deposits. This involves studying rock formations, soil samples, and other geological indicators to pinpoint areas rich in copper ore. Modern exploration techniques often employ advanced geophysical surveys, such as magnetic, gravity, and electromagnetic methods, to detect subsurface anomalies that might indicate mineral deposits.
Mining Methods
Once a copper deposit is located, mining engineers must determine the most efficient and safe method to extract the ore. Copper mines can be open pit or underground, depending on the depth and accessibility of the ore body.
- Open Pit Mining: This method is suitable for shallow ore bodies close to the surface. It involves excavating large pits to reach the copper ore, which is then removed using heavy machinery such as excavators and loaders.
- Underground Mining: When the copper ore is located deeper underground, miners dig shafts and tunnels to reach the ore. This method requires sophisticated ventilation and safety systems due to the confined spaces and potential for cave-ins.
Mining Process
The mining process for copper involves several key steps:
- Blasting: Once the ore body is accessed, explosives are used to break up the rock formation containing the copper. This process, known as blasting, is carefully planned to maximize ore recovery while minimizing damage to the surrounding rock.
- Crushing and Grinding: The blasted ore is then transported to a processing plant, where it is crushed into smaller pieces. This crushing process is followed by grinding the ore to a fine powder, increasing the surface area and enhancing the extraction efficiency.
- Flotation: The ground ore is mixed with water and a chemical reagent to create a slurry. This slurry is introduced into a flotation cell, where air bubbles are injected. The copper minerals attach to the bubbles and float to the surface, while the waste rock (known as tailings) settles at the bottom.
- Concentration and Dewatering: The copper-rich froth from the flotation process is collected and further concentrated by removing excess water. This concentrated copper ore, known as copper concentrate, is then ready for smelting.
- Smelting and Refining: The copper concentrate is fed into a furnace, where it is heated to high temperatures, separating the copper from other impurities. This process yields pure copper, which can then be refined further to produce copper cathodes or other copper products.
Environmental Considerations
Mining operations, especially copper mining, have significant environmental impacts. Mines must adhere to strict environmental regulations to minimize these impacts, including proper tailings management, water treatment, and rehabilitation of disturbed areas.
In conclusion, copper mining is a highly specialized and complex operation that requires precise planning and execution. From exploration to production, each step involves advanced technologies and rigorous safety measures to ensure efficient ore extraction while minimizing environmental impacts
