Common Methods of Weld Inspection 1. Eddy Current Eddy current testing (ET) is one of the non-destructive testing methods in industry Fast and effective detection of surface and subsurface cracks High detection rate without paint removal Wide coverage, fast scanning speed, save time Replace penetrant and magnetic particle testing 2. Industrial microscopes Check the cross section of the weld using our imaging solution All the measurements are completed in one step to realize fast detection Suitable for t-joints, lap joints and corner joints and all weld sizes Calibrate the image to obtain reliable results 3. Regular ultrasound High quality defect detection, very easy to use Its rugged, ergonomic design allows it to be used in challenging environments The intuitive interface is useful for both experienced and novice inspectors A full range of UT probes for detecting and measuring welding defects 4. Remote visual inspection Check hard-to-reach areas Best image quality […]
Welding
Methods to Prevent Welding Spatter 1. Prevention of CO2 welding spatter Using activated wire can refine metal droplet, reduce spatter and improve weld formation. The so-called activation treatment is a thin layer of alkaline earth metal or rare earth metal compounds on the surface of the welding wire to improve the ability of the welding wire to emit electrons. The most commonly used activator is cesium (CS) salts such as CSCO3, such as a little K2CO3, NA2CO3, the effect is more pronounced. The carbon content in the welding wire is limited to 0.08 ~ 0.11% . For this reason, the ultra-low carbon welding wire, such as Ho4mn2sitia, can be used. If necessary, use flux-cored wire to cover the surface of the droplet with slag to reduce spatter and make the weld in full bloom. Adding a small amount of AR gas into CO2 gas can improve the thermal characteristics and […]
10 Common Welding Problems and Solutions 1. Welding construction does not pay attention to select the best voltage Phenomenon: When welding, regardless of the backing, filling, cover, regardless of the size of groove, all choose the same arc voltage. This may not meet the requirements of the penetration, melting width, the occurrence of undercut, blowhole, spatter and other defects. Measures: Generally according to different circumstances should choose the corresponding long arc or short arc can get better welding quality and work efficiency. 2. Welding does not control welding current Phenomenon: When welding, in order to speed up the progress, for the thick plate butt weld to take no groove. The strength index drops, even can not reach the standard requirement, the crack appears in the bending test, which will make the performance of the welded joint can not be guaranteed, and pose potential harm to the structure safety. Measures: According […]
Four Position Welding Techniques 01 Backine welding Welding characteristics The molten metal falls due to gravity, and the shape and size of the molten pool can not be controlled. The surface of welding parts should not be welded flat. It is easy to have defects such as slag inclusion, non-penetration, welding tumor and poor weld formation. Melting weld metal spatter diffusion, easy to cause scalding accident. Backine welding is lower than other positions. 02 Downward welding Welding characteristics Weld metal mainly depends on the weight of the transition to the pool. The shape of molten pool and molten pool metal are easy to maintain and control. When welding the same thickness metal, the welding current at the flat welding position is larger than that at other welding positions, and the production efficiency is higher. Slag and molten pool are easy to appear mixing phenomenon, especially when welding fillet weld, slag […]
Causes and Control Methods of Welding Deformation of Steel Structure The type of deformation 1.Linear deformation Longitudinal deformation: is caused by longitudinal contraction of weld; Transverse deformation: is caused by transverse contraction of weld; 2.Angular distortion The upper layer of fillet weld has a large amount of welding and a large amount of shrinkage, so the fillet deformation is mainly caused by the uneven transverse shrinkage of the weld in its height direction. 3.Bending deformation For a t-shaped section, the contraction of the weld has an eccentricity to the center of gravity, thus bending the section upward, so the bending deformation is caused by the longitudinal contraction of the eccentricity weld. 4.Reverse the distortion In the welding process of steel structure, some special structural forms will appear wave-shaped or spiral-shaped deformation, which is called torsional deformation. Influence factors of welding deformation The main cause of welding deformation is the local […]
Why Low Carbon Steel can be Welded, High Carbon Steel can not be Welded Why Low Carbon Steel can be Welded, High Carbon Steel can not be Welded According to chemical composition, steel can be divided into carbon steel and alloy steel two categories. According to the chemical composition of steel can be divided into carbon steel and alloy steel two categories. Carbon Steel is divided into: Low carbon steel, carbon content less than 0.25% ; Medium carbon steel, carbon content of 0.25% ~ 0.6% ; High carbon steel, carbon content more than 0.6%. Mild steel is a kind of carbon steel whose carbon content is less than 0.25% . It is called soft steel because of its low strength and hardness. It consists of zero ordinary carbon structural steels and a portion of high-quality carbon structural steels. Medium Carbon Steel has good hot working and cutting properties and poor […]
Effects of Welding Parameters and Process on Weld Seam Effects of Welding Parameters and Process on Weld Seam: 1. The influence of welding current, arc voltage and welding speed on weld seam (1) Connect the current When the welding current increases (other conditions do not change) , the weld penetration and residual height increase, dissolve width does not change (or slightly increase) , the reasons are as follows: 1, the location of heat source moved down, and the penetration increased. The penetration depth is almost proportional to the current. With the increase of current, the melting amount of welding wire increases proportionally, and the residual height increases because the solution width is nearly constant. 3 with the increase of current, the diameter of arc column increases, but the depth of arc penetration into workpiece increases, the moving range of arc spot is limited, so the solution width is nearly constant. […]
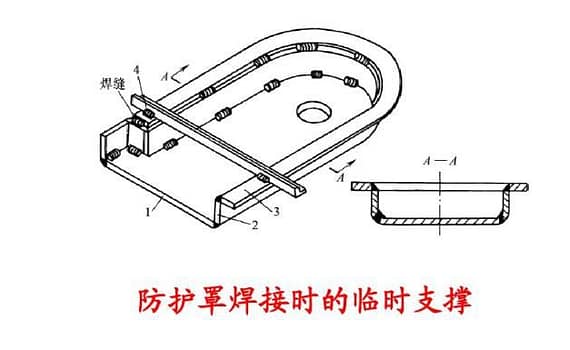
Weld Inspection – Efficiency 1 Cut – Weld Inspection – Efficiency Weld Inspection – Efficiency? Generally, flame cutting, as the main cutting technique, is the removal of more manageable welds from larger structures. In this case, it is important to cut macro/micro slices through the abrasive wet cutting process and to cut them well without being affected by any thermal burns caused by the main hot cutting operation. In order to minimize the deformation caused by cutting and the risk of thermal burn of cutting surface, it is usually recommended to select the appropriate cutting wheel and cutting parameters. 2 Mosaic – Weld Inspection – Efficiency The macroscopic sections used for procedural testing were prepared without mosaic, due to time constraints, and the finish from fine grinding was sufficient for macroscopic examination. If semi-automatic preparation is chosen, a number of sample holders are required to accommodate the unmounted sections of […]
Welding Inspection of Cryogenic Pressure Vessel and Points for Attention 1. Selection of welding materials Welding Inspection of Cryogenic Pressure Vessel – The selection of welding materials for low temperature pressure vessel steel must ensure that the welding joints contain the least harmful impurities such as sulfur, phosphorus, oxygen and nitrogen, will obviously reduce the toughness of the welded joint. When the load is large at low temperature, the same requirement should be applied to the non-pressurized accessory welding joint welded with the low-temperature pressurized component, and the welding material should be selected according to the welding requirement when the load is small. Low hydrogen basic electrodes for welding pressurized or pressurized components to non-pressurized components of cryogenic pressure vessels should be selected from the shielded metal arc welding of GHT5117“Carbon steel electrodes” and GBT5118“Low alloy electrodes”. Submerged arc welding flux should choose basic or neutral flux. 2. Product welding […]
Welding Quality Inspection – Sealing Test Welding quality inspection refers to the inspection of welding results to ensure the integrity, reliability, safety and usability of the welding structure. In addition to the requirements of welding technology and welding process, welding quality inspection is also an important part of welding structure quality management. This time we talk about the welding quality inspection method: sealing test. So how to detect the sealing of welded joint? In general, the following methods can be used for testing: 1. Submergence test Used for small vessels or pipes subject to less internal pressure. The vessel or pipe is filled with a Compressed air of pressure (0.4-0.5 MPA) prior to inspection, and then submerged to test the tightness, such as right leakage;. This is also a common part of the bicycle tube to check if there is a leak. 2. Water holding test The hydrostatic pressure generated […]
The Necessity of Ultrasonic Testing in Welding of Metallic Materials The Necessity of Using Ultrasonic Testing in Welding of Metallic Materials – There are many problems in the welding process of metal materials, the most important of which are three aspects: internal defects, macro defects, micro defects. In order to better analyze the importance of using ultrasonic nondestructive testing, we first look at these three aspects of defects in detail. Internal defects in welding of metallic materials The internal defects of the welding structure of metal materials are: slag residue left in the weld during workpiece welding, and one is in the process of material welding. A hole formed by encasing a gas in molten metal. Another is in the workpiece welding process between the material and the formation of cracks. Macroscopic defects in welding of metallic materials The macroscopic defects of the welding structure of metallic materials are: the […]
High Carbon Steel Welding Defects and Preventive Measures As high carbon steel tends to be hardened, it is easy to appear hot and cold cracks during welding. Measures to prevent thermal cracking Control the chemical composition of the weld, strictly control the content of sulfur and phosphorus, increase the content of manganese, in order to improve the weld structure and reduce segregation. Control the cross-section shape of the weld, width-depth ratio is slightly larger to avoid segregation of the weld center. Suitable welding parameters, welding sequence and welding direction should be selected for high rigidity welding parts. When necessary, take pre-heating and slow cooling measures to prevent the formation of hot cracks. Improve the alkalinity of electrode or flux, in order to reduce the impurity content in the weld, improve the segregation degree. Prevention of cold cracking Preheating before welding and cooling after welding can not only reduce the hardness […]
Abstract: This paper focuses on the Arctic LNG 2 project and its related fabrication and module yards in China. It explores the significance and challenges of this project, as well as the role played by Chinese yards in its implementation. Introduction: The Arctic LNG 2 project holds significant importance in the LNG industry. This study aims to examine the fabrication and module yards in China involved in this project. The Arctic LNG 2 Project Overview: A brief introduction to the project’s background and objectives. Discussing its scale and expected impact on the energy market. Fabrication and Module Yards in China: Identifying the key yards participating in the project. Exploring their capabilities and expertise in LNG fabrication. Technical Aspects and Challenges: Analyzing the technical requirements and challenges faced during the project. Highlighting the solutions adopted by the Chinese yards. Quality Control and Safety Measures: Discussing the importance of quality control and […]
Causes of Lamellar Tearing and How to Prevent? Causes of Lamellar Tearing and How to Prevent? Three general categories: The first one is lamellar tearing induced by cold crack at weld toe or root in haz. The second is the heat-affected zone along the inclusion cracks, is the most common engineering layered tearing. The third type of matrix crack far away from the heat-affected zone (haz) usually occurs in the thick plate structure with more MNS. There are many factors that affect lamellar tear, including: 1. The type, amount and distribution of non-metallic inclusions are the essential reasons of lamellar tearing, which is the root of anisotropy and mechanical properties difference of steel. 2. In the course of welding, the thick-wall welded structures with Z-constraint stress bear different Z-constraint stress, post-welding residual stress and load, which are the mechanical conditions that cause lamellar tearing. 3. It is generally believed that […]
What are the Welding Appearance Inspection Items? Weld is the bonding part of a welded piece. Weld can be generally divided into: flat weld, fillet weld, one-sided weld, one-sided weld double-sided shaped weld. The welds can also be divided into butt welds and fillet welds according to their own cross-sectional forms. Butt Welds: no penetration of the butt welds stress is very small, there is a serious stress concentration, penetration of the butt welds referred to as the butt welds. Fillet Weld: the connection plate edge need not finish processing, plate seamless, weld metal directly filled in the two pieces of welding form right angle or bevel in the region. The Weld appearance inspection can guide welders and welding inspectors to ensure the whole work and project welding quality. Welding appearance inspection items 1. Various welding defects Undercut: Groove or dent in base metal of weld toe due to improper […]
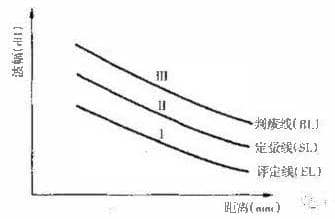
Analysis of the Types and Basic Characteristics of Welding Cracks With the development of steel, petrochemical industry, ship and electric power industry, the welding structure tends to be large-scale, large-capacity and high-parameter, some also work in low temperature, cryogenic, corrosive media and other environments. Therefore, all kinds of low-alloy high-strength steel, medium and high-alloy steel, super-strength steel, as well as a variety of alloy materials are increasingly widely used. However, with the application of these steels and alloys, there are many new problems in welding production, and the most common and serious one is welding crack. Cracks sometimes occur during welding, sometimes during placement or operation, and so-called delayed cracks. Because this kind of crack can not be detected in the manufacture, the harm of this kind of crack is more serious. There are many kinds of cracks in welding process. According to the present research, according to the nature […]
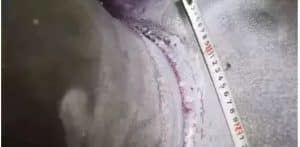
What is it Incomplete Penetration? Incomplete Penetration during welding refers to the defect caused by no melting between the base metal and the weld metal does not enter the root of the joint. According to the welding method of welding parts, it can be mostly divided into root and middle Incomplete Penetration. The root is not welded because the liquid weld metal does not enter the blunt edge of the root, most of them exist in the single side welding of the V-shaped or U-shaped groove, the middle is because the liquid metal does not enter the middle blunt edge, most of them exist in the double V or double U-sided welding. The existence of Incomplete Penetration in the weld will reduce the effective area, and seriously cause the mechanical properties of the decrease such as the strength of the welding parts. Incomplete Penetration will also cause stress concentration and […]
JSC is an ISO 17025 NDT Lab / Company (CNAS) ISO/IEC 17025:2017 is an international standard specifying requirements for quality and competence in testing and calibration laboratories. The standard requires that such labs prioritise excellent quality practices and develop a reliable quality management system to establish and demonstrate their competence. The full standard is called ISO/IEC 17025, since the certification was created by the International Organization for Standardization in conjunction with the International Electrotechnical Commission. However, many shorten this to ISO 17025 or simply 17025 certification when referring to the standard. Ultimately, ISO 17025 is for any organization that performs testing, sampling or calibration and wants to be sure of the reliability of their results. The simplest way we can put it: if you work in a testing environment that produces measurable results, then ISO 17025 is probably applicable. This may even mean you don’t necessarily call your facility a […]
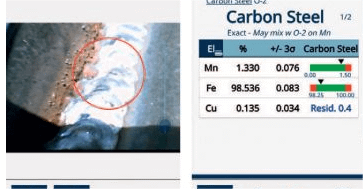
Steel plate base material (raw material) inspection is a crucial step in ensuring the quality and performance of steel products. This process involves a range of inspection methods, each with its own reference standards and key considerations. In this article, we will explore the advantages of steel plate base material (raw material) inspection, focusing specifically on the Q355B grade, and discussing various inspection techniques and their associated standards. Visual Inspection Firstly, let’s consider the visual inspection method. This involves a thorough examination of the steel plate’s surface for any visible defects or irregularities. Visual inspection is a quick and cost-effective way to identify potential issues, such as cracks, scratches, or discoloration. While it may not provide quantitative data, it serves as a valuable initial screening tool. Mechanical Testing Mechanical testing is another important aspect of steel plate base material (raw material) inspection. Tensile testing, for instance, measures the […]
Q235B and S235J0: Key Differences, Welding Considerations, Chinese Steel Mills’ Production and Advantages Q235B and S235J0 are two widely used structural steel grades, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the differences between these two grades, along with the production capabilities and advantages of Chinese steel mills, is crucial for making informed decisions in engineering projects. This article aims to delve into these distinctions, referencing their respective standards, highlighting welding considerations, and discussing the production and advantages of Chinese steel mills. Q235B and S235J0: Reference and Properties Q235B, according to the Chinese standard GB/T 700, is a carbon structural steel known for its strength and ductility. It is widely used in various structural applications in China and other Asian countries. On the other hand, S235J0, defined by the European Norm EN 10025, is a structural steel grade commonly found in European projects. Both grades have similar yield strengths but […]
Stainless Steel – Fabrication: An Insight into the Material and Key Considerations During Fabrication Stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance and durability, is a crucial material in the fabrication industry. Its unique properties make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial equipment to architectural structures. In this article, we will delve into the nature of stainless steel, explore its fabrication process, and highlight the key considerations during the process. What is Stainless Steel? Stainless steel is an alloy of iron with a minimum of 10.5% chromium. The chromium content forms a thin, invisible, corrosion-resistant layer on the steel’s surface, protecting it from oxidizing and rusting. In addition to chromium, stainless steel may also contain other elements such as nickel, molybdenum, titanium, and nitrogen, which further enhance its properties. Stainless steel is classified into several types based on its composition and properties. The most common types include […]
Pressure Vessels, Tanks, Skids – Fabrication: An Insight into the Process and Key Considerations Pressure vessels and tanks are essential components in various industries, such as petrochemical, refining, chemical processing, and power generation. These vessels and tanks are designed to store fluids or gases under pressure and must, therefore, be fabricated with utmost precision and care. In this article, we will delve into the fabrication process of pressure vessels and tanks, highlighting the key points that need to be considered during the process. What are Pressure Vessels & Tanks? Pressure vessels and tanks are closed containers designed to hold fluids or gases at a pressure higher than the ambient atmospheric pressure. They are made from various materials, including steel, stainless steel, and alloys, depending on the specific application and the type of fluid or gas they are designed to hold. These vessels and tanks come in a range of […]
How to Explain the Cause of the Welding Defects on the Negative Plate 1. Common welding defects can be classified into four categories: 1) Weld size does not meet the requirements: such as ultra-high, ultra-wide, too narrow, too large difference between height and height, weld transition to the base metal is not smooth. 2) Welding surface defects: such as undercut, Weld, concave, overflowing, no penetration, surface porosity, surface cracks, etc. . 3) Weld internal defects: such as porosity, slag inclusion, cracks, non-fusion, tungsten inclusion, double-sided welding, such as the lack of penetration。 4) The properties of welded joint do not meet the requirements: the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of welded joint are reduced because of over-heating and over-burning. 2. The damage of welding defects to welded components mainly includes the following a spects: 1) Cause stress concentration The distribution of stress in welded joint is very complex. Where there […]
Welding defects refer to various discontinuities, imperfections, or poor connections in the welded joint that occur during the welding process. These defects can include incomplete fusion, porosity, slag inclusion, undercut, overlap, burn-through, segregation, incomplete filling, and welding cracks, among others. Among these defects, welding cracks and porosity pose the greatest hazards to the performance and safety of welded structures. Welding cracks are gaps that form in the welded joint due to the breakdown of the atomic bonds between metals, caused by welding stresses and other brittleness-inducing factors. Depending on their nature, welding cracks can be classified into various types such as hot cracks, cold cracks, reheat cracks, lamellar tearing, and stress corrosion cracks. For example, hot cracks occur at high temperatures during the welding process. Their shape and temperature zone vary depending […]
Post-weld Heat Treatment is not Entirely Advantageous Post-weld heat treatment – Welding residual stress is caused by non-uniform temperature distribution, thermal expansion and contraction of weld metal, so it is inevitable to produce residual stress with welding construction. The most common method to eliminate residual stress is high-temperature tempering, in which the weldments are heated to a certain temperature and held for a certain time in a heat treatment furnace, taking advantage of the reduction of the yield limit of the material at high temperature, when the internal stress is high, the plastic flow will occur, the elastic deformation will decrease, and the plastic deformation will increase and the stress will decrease. 1) Selection of heat treatment methods The influence of post-weld heat treatment on tensile strength and creep limit of metal is related to the temperature and holding time of heat treatment. The effect of post-weld heat treatment on […]
Why porosity / porosities often appear in welds? Reason 1: The gas is impure Porosity – Preventive measures: gas cylinders regularly clean, in the use of gas cylinders inverted 1-2 hours before opening the valve after the water after use. Reason 2: Surface Oil and rust Preventive measures: cleaning the surface of the workpiece before welding oil, rust, oxide, etc. . Can be used wire brush, shot blasting and other methods to remove. Reason 3: Blocked air passage or air leak Preventive measures: often check the gas system is blocked or gas leakage. Timely cleaning, maintenance or replacement, develop good operating habits. Reason 4: Seal weld without vent hole Prevention measures: butt welding will increase chamfer, the middle does not leave air gap. Leave out part of the weld without welding or until the workpiece cools before welding. Reason 5: Welding Torch angle is too small, air from the rear […]
All Kinds of Welding Defects Diagram and How to Prevent Welding Defects Diagram and How to Prevent – Causes of incomplete penetration The main causes of non-penetration are: small groove angle, too narrow root gap or too thick blunt edge, improper selection of welding current is too small, line energy is small, welding speed is too fast. 1、Cold Crack The characteristics of cold cracks are mostly in the heat affected zone near the fusion line between weld bead and base metal, and most of them are transgranular cracks. Cold crack without oxidation color. Cold cracks occur at or with high carbon and alloy content. Cold cracks have a delayed nature, mainly delayed cracks. The quenching tendency of cold crack (and heat affected zone and fusion zone) is serious, resulting in quenching microstructure and embrittlement of joint. High hydrogen content, and gathered in place to form a large number of hydrogen […]