Paint Adhesion – Cross Cut Test
In the world of coatings and paints, adhesion is a crucial factor that determines the durability and long-term performance of a coating system. The Cross Cut Test, also known as the Cross Hatch Test, is a widely used method to assess paint adhesion, providing crucial insights into the bond strength between the paint film and the underlying substrate.
What is the Cross Cut Test?
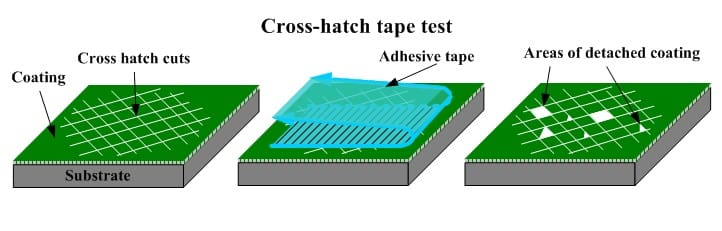
The Cross Cut Test is a standardized procedure for evaluating paint adhesion by creating a grid-like pattern on the paint film using a cutting tool. This grid pattern is then visually inspected to determine the degree of paint film removal when subjected to a specified force, typically by applying a tape pull or a fingernail scratch.
Why is Paint Adhesion Important?
Paint adhesion is critical for ensuring the integrity and durability of painted surfaces. A poorly adhering paint film is prone to peeling, chipping, and cracking, which not only compromises the aesthetics but also exposes the substrate to potential corrosion and degradation. Therefore, accurate assessment of paint adhesion is essential for quality control and product development.
How Does the Paint Adhesion Cross Cut Test Work?
The Cross Cut Test involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The test surface is thoroughly cleaned and prepared according to the paint manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Application: The paint is applied evenly and allowed to dry completely.
- Cutting: Using a standardized cutting tool, a grid pattern is created on the paint film, typically consisting of parallel cuts at right angles to each other.
- Inspection: The grid pattern is visually inspected for any paint film removal or lifting. The extent of removal is classified based on standardized rating scales.
- Interpreting the Results of the Cross Cut Test
The results of the Cross Cut Test are typically expressed using a rating scale that ranges from 0 to 5, where 0 indicates complete paint removal and 5 represents no paint removal. Each rating corresponds to a specific degree of paint film removal, providing a quantitative measure of paint adhesion.
Factors Affecting Paint Adhesion
Paint adhesion is influenced by a variety of factors, including:
Substrate properties: The surface energy, roughness, and chemical composition of the substrate can significantly impact paint adhesion.
Paint formulation: The choice of binders, pigments, additives, and solvents in the paint formulation can affect adhesion properties.
Application conditions: Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and cleanliness during paint application can influence adhesion.
Strategies for Improving Paint Adhesion
To enhance paint adhesion, several strategies can be employed:
Select a paint formulation that is compatible with the substrate material.
Ensure proper surface preparation by cleaning and preparing the substrate according to manufacturer’s recommendations.
Apply the paint in optimal conditions, considering factors like temperature, humidity, and ventilation.
Use primers or adhesion promoters to enhance the bond between the paint film and the substrate.
The Importance of Standardization in the Paint Adhesion Cross Cut Test
Standardization is crucial in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the Cross Cut Test results. Using standardized cutting tools, rating scales, and inspection procedures ensures consistency in testing and allows for comparison of results across different substrates, paint formulations, and application conditions. This standardization is essential for quality control, product development, and comparison of different coating systems.
In conclusion
the Cross Cut Test is a valuable tool for assessing paint adhesion, providing crucial insights into the bond strength between the paint film and the underlying substrate. By understanding the principles and procedures of this test, as well as the factors that influence paint adhesion, paint manufacturers and coating professionals can develop and apply coating systems that exhibit excellent adhesion properties, ensuring the durability and long-term performance of painted surfaces. resources.
Learn more Successful Arctic module fabrication, steel structure, modular and skid, steelwork, supplier audit, DNV Class, Oil & Gas, welding supervisor, welding quality inspection, CWI CSWIP welding inspector, pump and pipe, stainless steel fabrication and CNAS ISO 17025 9712 NDT NDE practice via below-
https://www.jsc-safe.com/steel-structures-modules-machining/
