Introduction of Adhesion Testing Methods
Adhesion is a critical property in various industries, ensuring the durability and reliability of coatings, adhesives, and bonded materials. Evaluating adhesion requires precise testing methods to assess the strength of bonds between different surfaces. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various Adhesion Testing Methods used, referencing international standards such as ISO, Australian Standards, and American Standards.
Importance of Adhesion Testing
Before delving into specific testing methods, it’s crucial to understand why adhesion testing is essential. Adhesion strength determines the performance and longevity of coatings and adhesives, impacting product quality and safety. Poor adhesion can lead to product failure, structural damage, and safety hazards. By evaluating adhesion, manufacturers can ensure compliance with industry standards and meet customer expectations.
Adhesion Testing – Peel Test
The peel test is one of the most commonly used methods to evaluate adhesion, particularly for flexible materials like tapes and films. This test measures the force required to peel apart two bonded surfaces at a specified angle and speed. ISO 8510-1:2012 outlines the procedure for conducting peel tests, providing guidelines for sample preparation, testing conditions, and data analysis.
Adhesion Testing – Pull-Off Test
The pull-off test, also known as the tensile adhesion test, assesses the bond strength between a coating and its substrate. This method involves applying a perpendicular force to the coating surface using a specialized instrument, such as a pull-off adhesion tester. ASTM D4541/D4541M-17 outlines the standard test method for performing pull-off tests on coatings using portable adhesion testers.
Shear Test
Shear testing evaluates the adhesion strength of bonded materials subjected to parallel forces, simulating real-world conditions more accurately. ASTM D1002-10 provides guidelines for conducting shear tests on adhesively bonded joints, including sample preparation, testing procedures, and data analysis. Shear testing is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction to assess the integrity of bonded assemblies.
Cohesion Test
While most adhesion tests focus on the bond between two different materials, cohesion tests evaluate the internal strength of a single material. These tests involve subjecting the material to forces that induce internal failure, such as tensile or compressive forces. ASTM D897-18 outlines the standard test method for determining the cohesive strength of adhesive bonds using a T-peel test fixture.
Scratch Test
The scratch test assesses the resistance of coatings and films to damage caused by abrasive forces. This method involves scratching the surface with a sharp or abrasive tool and measuring the force required to penetrate or remove the coating. ISO 19252:2019 specifies the procedure for conducting scratch tests on paint coatings using various scratch tools and evaluating the results based on scratch depth and width.
Cross-Cut Test
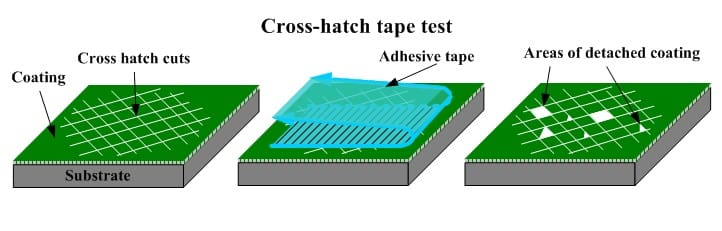
The cross-cut test, also known as the lattice or grid test, evaluates the adhesion of coatings to substrates by making a series of intersecting cuts through the coating layer. After cutting, adhesive tape is applied to the surface and then removed, determining the extent of coating adhesion. ASTM D3359/D3359M-17 outlines the standard test methods for performing cross-cut adhesion tests on paint coatings.
Contact Angle Measurement
Contact angle measurement is a surface-sensitive technique used to assess the wettability and adhesion properties of solid surfaces. By measuring the angle formed between a liquid droplet and the surface, researchers can infer the surface energy and adhesion characteristics. ASTM D7334-08 provides guidelines for measuring contact angles using various methods, including sessile drop, captive bubble, and Wilhelmy plate techniques.
Microscopy and Imaging Techniques
Microscopy and imaging techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM), offer valuable insights into the morphology and adhesion behavior of materials at the micro and nanoscale. These techniques allow researchers to visualize interfacial interactions, surface roughness, and failure mechanisms, enhancing our understanding of adhesion processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, evaluating adhesion is essential for ensuring the quality, reliability, and safety of coated and bonded materials across various industries. By employing a combination of standardized testing methods, including peel, pull-off, shear, cohesion, scratch, and contact angle tests, manufacturers can accurately assess adhesion properties and meet stringent quality standards. Incorporating advanced techniques such as microscopy and imaging further enhances our understanding of adhesion mechanisms, driving continuous improvement and innovation in material science and engineering integrity and performance surfaces. resources.
Learn more Successful Arctic module fabrication, steel structure, modular and skid, steelwork, supplier audit, DNV Class, Oil & Gas, welding supervisor, welding quality inspection, CWI CSWIP welding inspector, pump and pipe, stainless steel fabrication and CNAS ISO 17025 9712 NDT NDE practice via below-
https://www.jsc-safe.com/steel-structures-modules-machining/
